Myocarditis is a condition in which the heart muscle becomes inflamed, interfering with the heart’s ability to pump blood and maintain a stable rhythm. The severity of myocarditis varies widely—from mild, self-limited illness to severe heart failure or dangerous arrhythmias.
Myocarditis often affects otherwise healthy individuals and may follow a recent viral infection. Because symptoms can be subtle or mimic other conditions, early recognition is important.
How Myocarditis Affects the Heart
Inflammation within the heart muscle disrupts normal contraction and relaxation. Swelling and cellular injury reduce pumping efficiency, while inflammation can irritate the heart’s electrical system, increasing the risk of rhythm disturbances.
In some cases, the heart recovers fully after the inflammation resolves. In others, ongoing injury may lead to scarring, chronic heart weakness, or Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
Common Causes of Myocarditis
Myocarditis has many potential causes, but viral infections are the most common worldwide.
Common causes include viral infections, immune-mediated reactions, certain medications or toxins, and systemic inflammatory diseases. Less commonly, bacterial or parasitic infections may be responsible.
In many patients, a specific cause is never identified, even after thorough evaluation.
Symptoms of Myocarditis
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may develop days to weeks after an infection.
Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath at rest or with exertion
- Fatigue and weakness
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Dizziness or fainting
Some people experience only mild symptoms, while others develop rapid worsening of heart function.
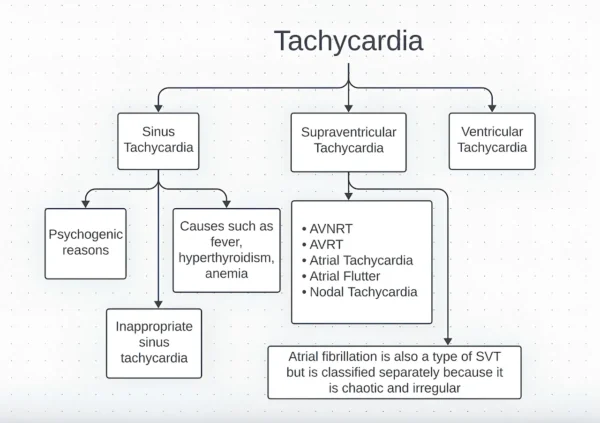
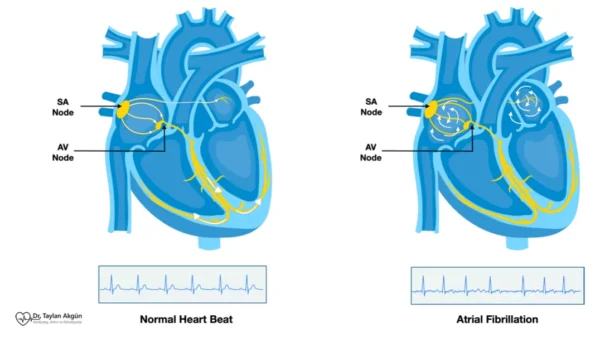
Myocarditis and Arrhythmias
Inflammation can disrupt the heart’s electrical pathways, leading to arrhythmias. Both atrial and ventricular rhythm disturbances may occur, sometimes causing palpitations, fainting, or sudden collapse.
Arrhythmias may be temporary during the inflammatory phase or persist if scar tissue develops.
How Myocarditis Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis is based on clinical suspicion, imaging, and laboratory testing. Echocardiography is used to assess heart function and detect weakness or fluid accumulation.
Cardiac MRI plays a key role by identifying inflammation, swelling, and scar tissue within the heart muscle. Blood tests may show markers of inflammation or heart muscle injury.
In selected cases, additional testing is required to clarify the diagnosis or rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Myocarditis
Treatment of myocarditis depends on the severity of inflammation, the degree of heart involvement, and the underlying cause. Management ranges from supportive care and close observation to advanced therapies in severe cases.
Rest and Activity Restriction
In mild cases, treatment begins with strict physical rest and temporary restriction of physical activity. This allows the inflamed heart muscle time to heal and reduces the risk of worsening inflammation or dangerous arrhythmias.
Patients are typically advised to avoid intense exercise and competitive sports for several weeks to months. The duration of activity restriction depends on symptom resolution and follow-up testing, not just how the patient feels.
Medication Therapy
Medications are commonly used to support heart function and manage symptoms during recovery.
Depending on the clinical presentation, medications may be prescribed to:
- Reduce strain on the heart and improve pumping efficiency
- Control fluid retention if heart failure symptoms are present
- Manage abnormal heart rhythms
- Relieve chest discomfort or inflammation
These treatments do not directly “cure” myocarditis but help stabilize the heart while inflammation resolves. Medication regimens are adjusted over time based on recovery and follow-up findings.
Hospitalization and Monitoring
Patients with moderate to severe myocarditis may require hospitalization for close monitoring. This is especially important if there are signs of heart failure, significant rhythm disturbances, or reduced heart pumping function.
In the hospital setting, continuous heart rhythm monitoring allows early detection and treatment of arrhythmias. Supportive therapies are provided as needed until the heart stabilizes.
Advanced Therapies in Severe Myocarditis
In rare but serious cases, myocarditis can cause rapid deterioration of heart function. When this occurs, advanced therapies may be required.
These can include intensive medical support, temporary mechanical circulatory support devices, or other specialized treatments aimed at maintaining circulation while the heart recovers. Such cases are managed in experienced centers.
Duration of Treatment and Recovery
Recovery from myocarditis is highly variable. Some patients improve within weeks, while others require months of treatment and follow-up. Improvement in symptoms does not always mean full recovery of the heart muscle.
Follow-up imaging and heart rhythm monitoring are often used to confirm recovery before normal physical activity is resumed. Ongoing follow-up helps identify patients who develop persistent heart weakness or long-term complications.
Importance of Avoiding Early Return to Exercise
Avoiding intense physical activity during recovery is critical. Exercising too soon can worsen inflammation, delay healing, and significantly increase the risk of serious arrhythmias.
Return to exercise is usually gradual and guided by medical evaluation rather than symptoms alone.
Recovery and Long-Term Outlook
Many people with myocarditis recover completely, especially when the condition is recognized early and managed appropriately. Recovery may take weeks to months.
Some individuals develop persistent heart dysfunction and require long-term follow-up and treatment. Regular monitoring helps assess recovery and guide safe return to normal activity.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Chest pain, unexplained shortness of breath, fainting, or new palpitations—especially following a recent infection—should prompt medical evaluation. Early assessment improves outcomes and reduces the risk of complications.
In Summary
Treatment of myocarditis focuses on rest, supportive medical therapy, and careful monitoring while the heart heals. Most patients recover fully, but the healing process takes time and requires patience. Adhering to activity restrictions, medication plans, and follow-up appointments is essential to protect long-term heart health.
Reference: Myocarditis