Heart Attack and Arrhythmias
A heart attack and cardiac arrhythmias share a close, bidirectional…
Cardiac Electrophysiologist
Prof. Dr. Taylan Akgün is a cardiologist specialized in electrophysiology, with extensive experience in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. He has particular expertise in advanced electrophysiological procedures such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular extrasystole (VES), supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), and cardioneuroablation (CNA) used in the treatment of vasovagal syncope.
Throughout his career, he has performed over 10,000 ablation procedures, as well as thousands of pacemaker, implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), and cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device implantations. He currently serves patients in Istanbul.

Prof. Dr. Taylan Akgün has been actively involved in the diagnosis and treatment of heart rhythm disorders for more than 20 years.
Through his national and international publications, he contributes academically to the field of cardiac electrophysiology.

A heart attack and cardiac arrhythmias share a close, bidirectional…
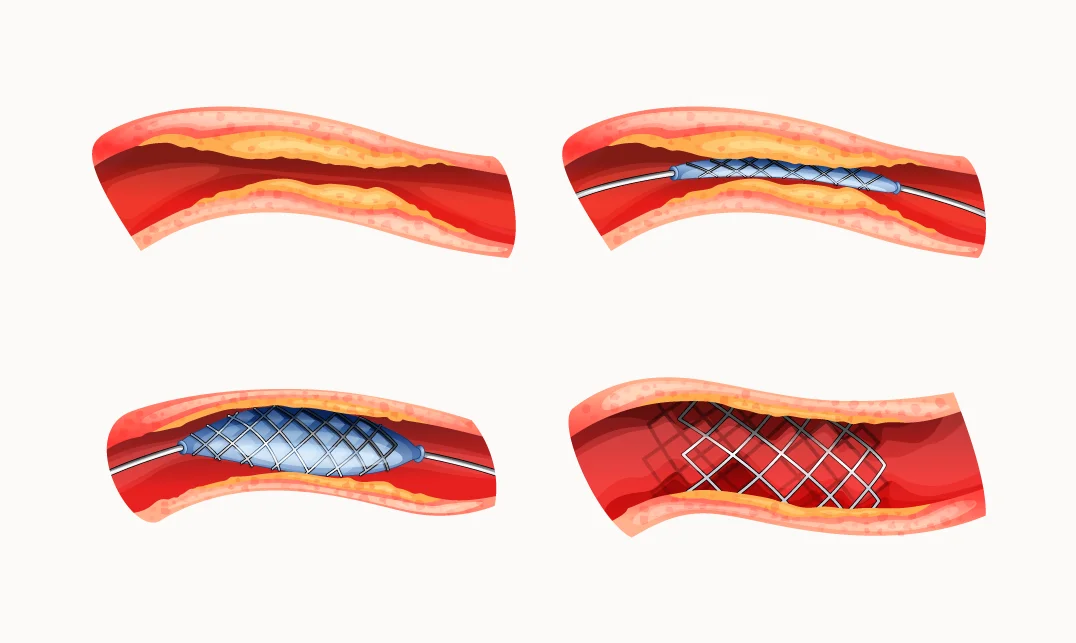
Coronary stent placement is an effective treatment for restoring blood…
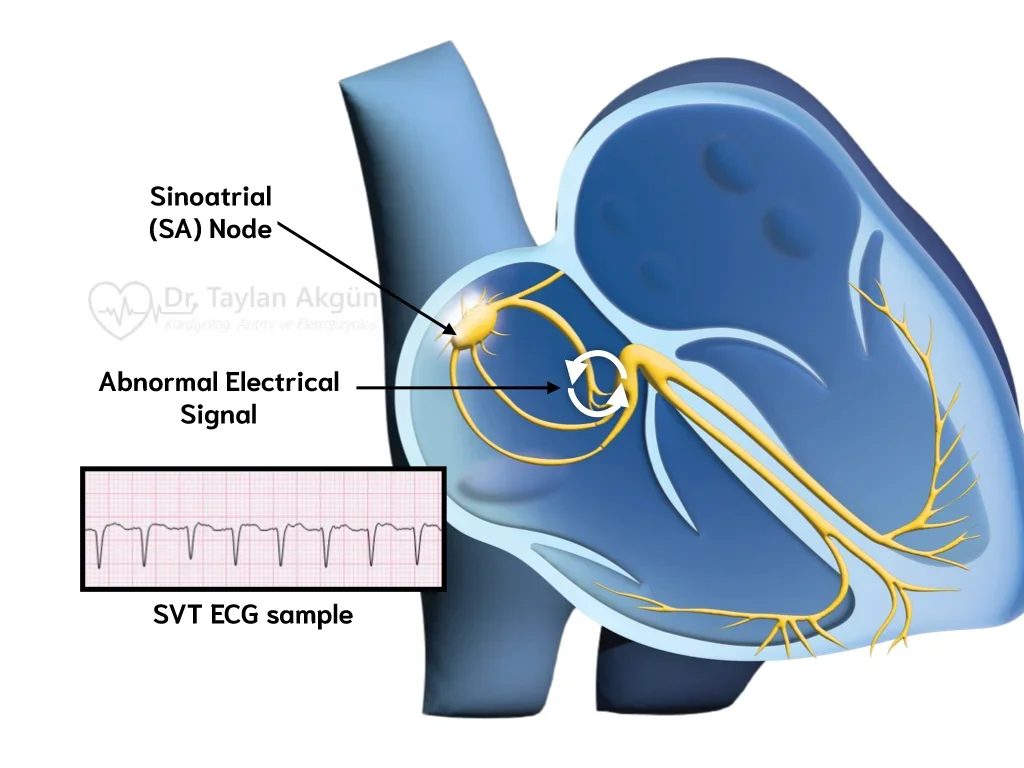
SVT Ablation SVT ablation is a catheter-based procedure that eliminates…
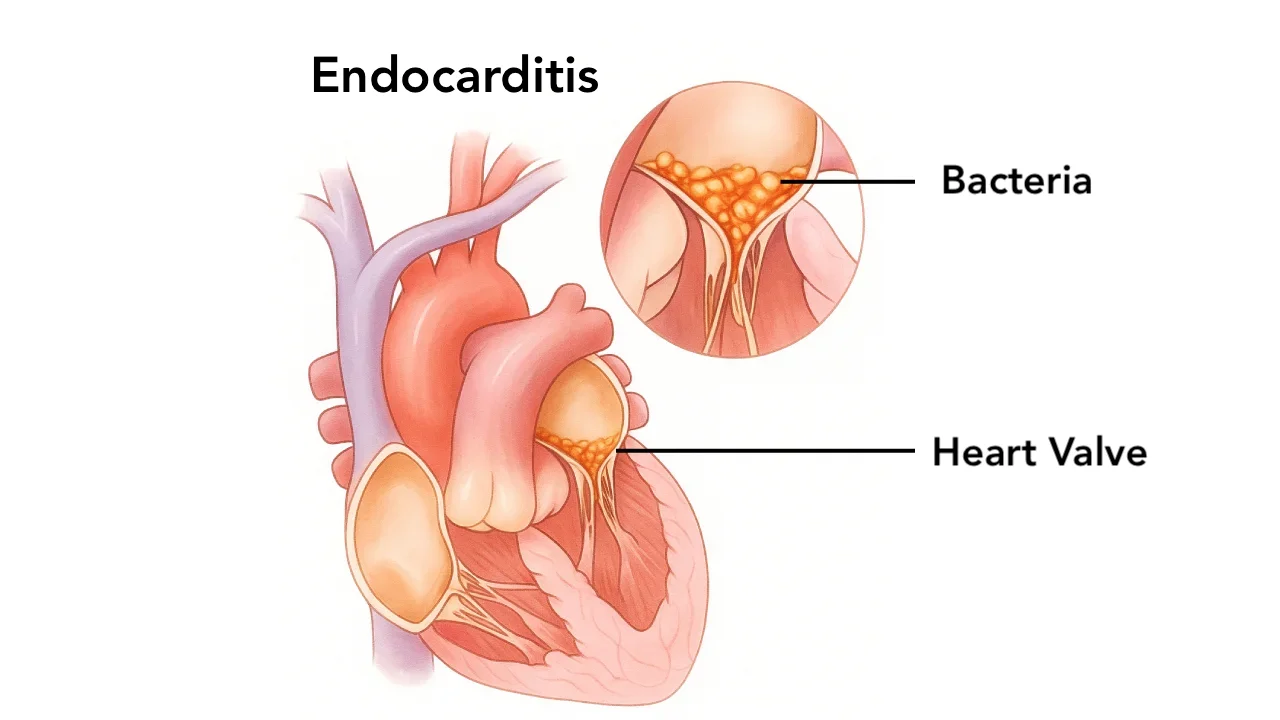
What Is Endocarditis Prophylaxis? Endocarditis prophylaxis refers to the administration…
Our HOMA-IR calculator estimates your level of insulin resistance using your…
What Is a Heart Attack Risk Calculator? The ASCVD heart…

Sleep Quality Calculator This sleep quality calculator evaluates your sleep…

Metabolic Age Calculator The metabolic age calculator evaluates your body…
You can access various online health calculators that help evaluate your body and heart health by using the button below.
You can easily calculate your body mass index (BMI), insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), 10-year heart attack risk (ASCVD), sleep quality, metabolic age, and metabolic rate.
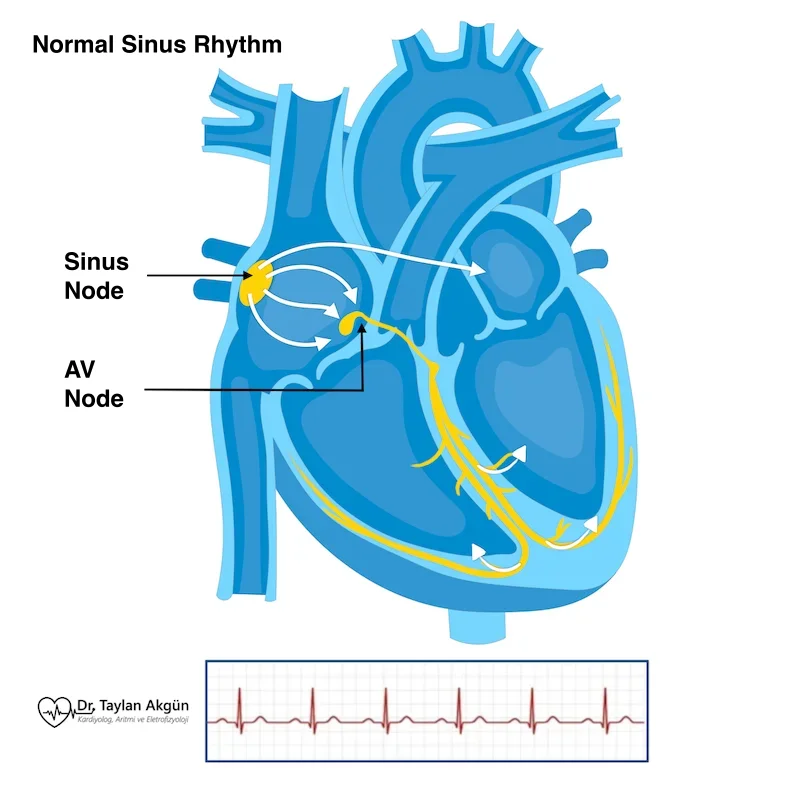
Cardiac electrophysiology is a subspecialty of cardiology that focuses on the heart’s electrical system and the diagnosis and treatment of heart rhythm disorders (arrhythmias).
Procedures in this field are performed to evaluate the heart’s electrical conduction, identify abnormal heart rhythms, and treat them when necessary.
The heart's normal rhythm and blood circulation are maintained by the electrical system within the heart. An electrophysiologist is a cardiologist who specializes in diagnosing and treating problems with the heart's electrical system.
An electrophysiologist diagnoses and treats problems in your heart's electrical system. They identify the cause of rhythm or conduction disorders. These rhythm disorders can range from very mild to life-threatening. Once the cause is found, they correct your rhythm and conduction disorder through medical treatment, catheter ablation, and pacemaker therapies. Successful treatment can be achieved in more than 90% of rhythm problems. This results in a significant improvement in your quality of life.
The most important step in detecting cardiac arrhythmias is having a detailed discussion with the patient about their complaints, questioning the onset, end, and what happens during the complaint. Arrhythmias sometimes continue for a while and then stop. Tests performed after they stop may come back normal. This doesn't mean there isn't an illness. An electrophysiologist performs certain tests to understand exactly what's causing your problem. These include:
An electrophysiologist treats most disorders in your heart rhythm. These are usually conditions where the heart beats too fast or irregularly. While some rhythm disorders are annoying and affect your quality of life, others pose fatal risks. The conditions treated include:
You should see an electrophysiologist especially if you have complaints such as heart palpitations, skipped heartbeats, irregularity in pulse or heartbeats, shortness of breath, decreased exercise capacity, early fatigue, fainting, or near-fainting episodes. However, it should be remembered that symptoms in heart diseases can be similar. The electrophysiologist determines whether these complaints are due to arrhythmia through the tests they perform.