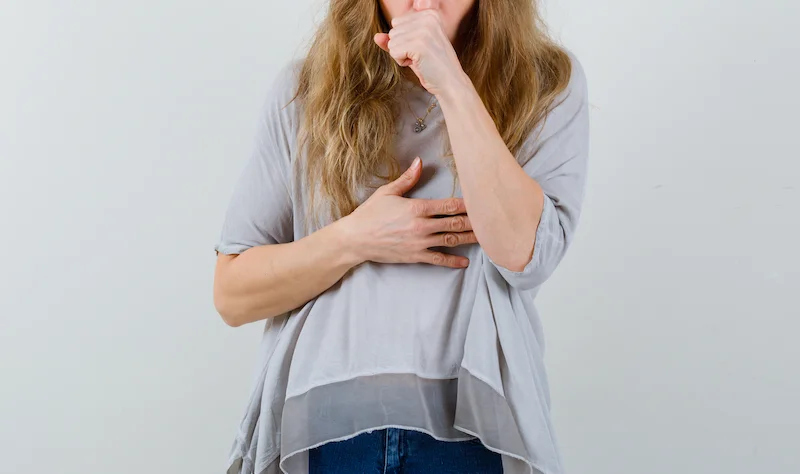
Shortness of breath is the sensation of not getting enough air or having difficulty breathing. In medical terms, it is called dyspnea. It may develop suddenly or gradually over time.
Shortness of breath can have many different causes. Some are mild and temporary, while others require urgent medical attention. Sudden and severe shortness of breath can be a serious medical condition. Do not delay seeking help.
How does shortness of breath feel?
If you have shortness of breath, you may experience the following sensations:
- A feeling of tightness in the chest
- Inability to get enough air
- Increased effort to breathe
- Rapid or shallow breathing
- A sensation of suffocation
- Difficulty speaking
- Shortness of breath that worsens with exertion
Shortness of breath may also be accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, cough, wheezing, fatigue, or dizziness.
Call emergency services immediately if:
- Sudden and severe shortness of breath begins
- Chest pain accompanies the shortness of breath
- Your lips or fingers turn bluish
- You cannot speak or form full sentences
- You feel confused
- You feel like you are about to faint
- You have swelling and pain in one leg (risk of deep vein thrombosis)
Do not drive yourself to the emergency department.
Causes of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath has many possible causes.
Common causes include:
- Asthma
- Chest infections
- Allergies
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Panic attacks
- Anemia
However, in some cases, shortness of breath may be a sign of a more serious condition, such as:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Heart failure
- Heart attack
- Blood clot in the lungs (pulmonary embolism)
- Lung cancer
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Do not try to diagnose the cause of shortness of breath on your own. Always consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of shortness of breath
Your doctor will first take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination. They will ask when the shortness of breath started, how long it lasts, and which situations make it worse.
To determine the cause, some of the following tests may be performed:
- Chest X-ray
- Blood tests
- ECG (electrocardiogram)
- Pulmonary function tests (spirometry)
- Heart ultrasound (echocardiography)
- Computed tomography (CT scan)
- D-dimer test (if a blood clot is suspected)
The choice of tests depends on your symptoms and physical examination findings.
Treatment of shortness of breath
Treatment varies depending on the underlying cause.
In sudden (acute) shortness of breath:
- Oxygen therapy may be given if blood oxygen levels are low
- Bronchodilator medications may be used if the airways are narrowed
- Antibiotics may be started if infection is the cause
- Emergency treatment is provided if you are having a heart attack
- Blood thinners are used if a pulmonary embolism is diagnosed
In persistent (chronic) shortness of breath:
- Regular medication is used if asthma or COPD is present
- Heart medications are prescribed for heart failure–related shortness of breath
- Home oxygen therapy may be required if oxygen levels remain low
- Pulmonary rehabilitation programs may be recommended
- Weight loss programs may be advised if excess weight contributes to symptoms
- Psychological support may help if anxiety or panic attacks are the cause
Medications may take time to become effective. Adhering to treatment regularly is essential.
What helps relieve shortness of breath?
To reduce the severity of shortness of breath, you can:
- Quit smoking (smoking causes significant lung damage)
- Avoid triggers (pollen, dust, perfumes)
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Exercise regularly (after consulting your doctor)
- Take medications as prescribed
- Practice stress management techniques
- Drink adequate fluids
- Sleep with your head elevated (especially in heart failure)
Regular exercise can increase lung capacity and help reduce shortness of breath over time.
What to do during a shortness of breath episode
If your shortness of breath worsens:
- Try to stay calm (panic makes symptoms worse)
- Sit down and lean forward (this position helps breathing)
- Breathe slowly through pursed lips
- Open a window for fresh air
- Wear loose clothing
- Use your asthma inhaler if prescribed
- Call emergency services if there is no improvement
The pursed-lip breathing technique is especially helpful for patients with COPD.
Frequently asked questions
Can shortness of breath be related to stress?
Yes. Shortness of breath is common during anxiety and panic episodes. However, organic causes must always be ruled out first.
Which doctor should I see for shortness of breath?
Initial evaluation can be performed by a family physician or internal medicine specialist. If needed, you may be referred to pulmonology, cardiology, or other specialties.
Reference: Dyspnea