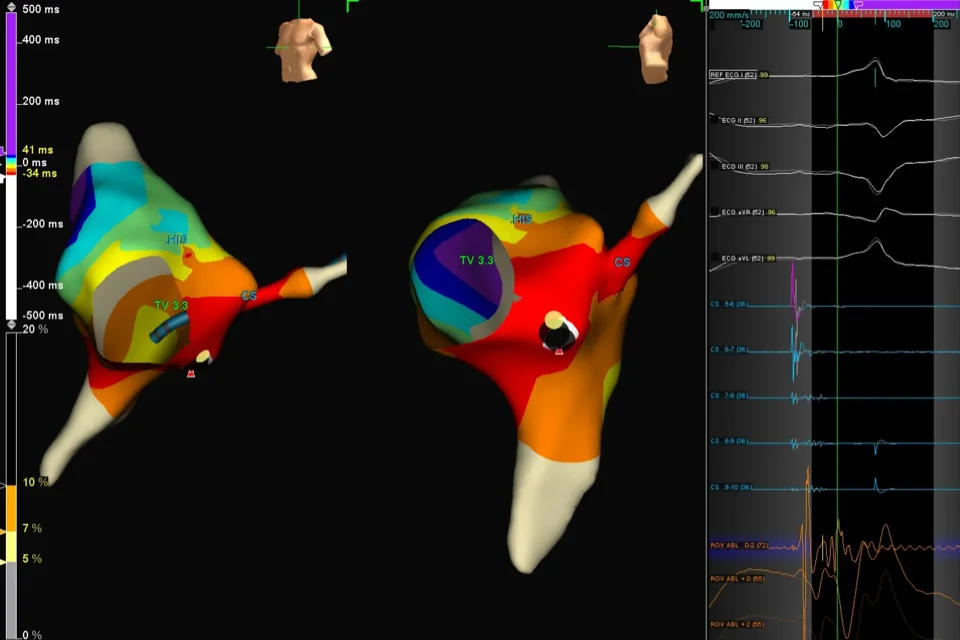
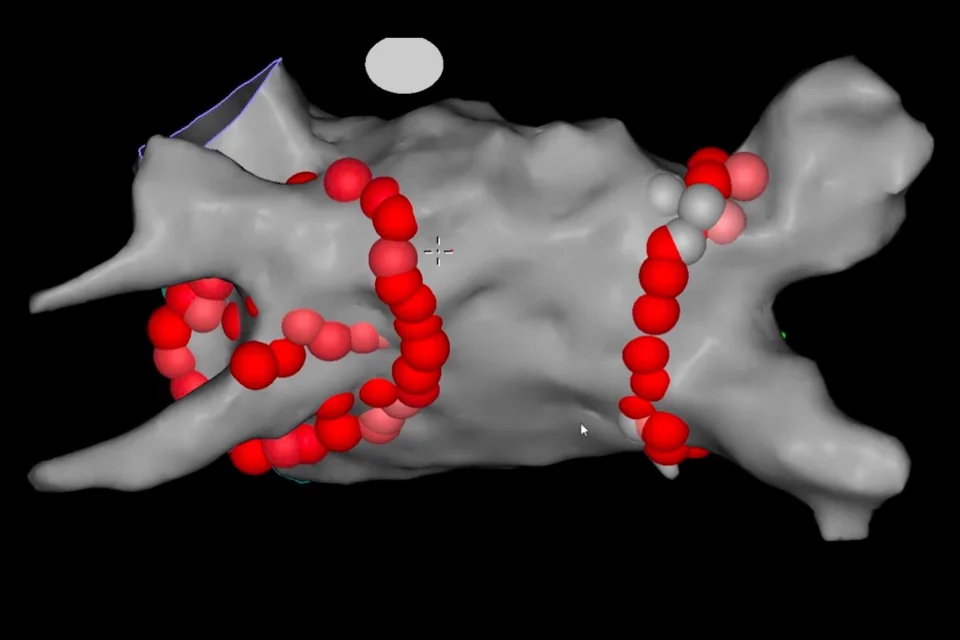
When doctors perform cardiac ablation to fix abnormal heart rhythms, they need to know exactly where the problem is coming from. Traditional ablation uses X-rays and basic electrical recordings to locate problem areas, but this provides limited information. 3D mapping creates a detailed, color-coded three-dimensional picture of your heart’s electrical activity, showing precisely where abnormal signals originate and how they travel. Special catheters record electrical signals from hundreds of points inside your heart. A computer combines this data into a 3D model displayed on screens, looking like a colorful map of your heart’s interior. The map shows normal areas in one color and abnormal areas causing rhythm problems in different colors.
Overview
3D mapping is advanced technology that creates detailed three-dimensional pictures of your heart’s electrical activity during ablation procedures. This provides far more information than traditional methods.
During traditional ablation, doctors use X-ray images showing your heart’s outline and basic catheters recording electrical signals from a few spots. This works but provides limited detail. Imagine trying to navigate a city with only a rough sketch showing a few streets—you know the general area but lack precise details.
3D mapping systems are like having detailed GPS navigation. They create comprehensive electrical maps of your heart chambers showing exactly where signals originate, how they travel, and which areas are causing problems.
Special mapping catheters with multiple electrodes touch your heart walls at hundreds of different points. At each point, they record the electrical signal’s timing, strength, and direction. A powerful computer combines all these measurements into a 3D model of your heart chamber.
The model appears on large screens in the procedure room. Doctors see a rotating, color-coded picture of your heart’s interior. Colors represent timing—areas activating early appear in one color, areas activating late appear in different colors. Abnormal areas causing rhythm problems show distinctive patterns.
The system also tracks catheter positions in real-time. As doctors move catheters inside your heart, their positions appear on the 3D map. This lets doctors navigate precisely without relying solely on X-rays, reducing radiation exposure.
Once problem areas are identified on the map, doctors use ablation catheters to destroy those specific spots. The map guides treatment with precision, ensuring complete treatment of problem areas while avoiding unnecessary damage to healthy tissue.
Several 3D mapping systems exist—CARTO, EnSite, and Rhythmia are the most common. Each works slightly differently but provides similar detailed mapping capabilities.
How It Works During Your Procedure
Understanding what happens helps you appreciate the technology, even though you’re sedated during the procedure.
After catheters are positioned in your heart, the mapping phase begins. A specialized mapping catheter is moved systematically around the inside of your heart chamber, touching the walls at many points.
The catheter might have a basket-like structure with multiple electrodes that expand inside your chamber, recording from many points simultaneously. Or it might be a catheter with electrodes at the tip that touches hundreds of points sequentially, building the map point by point.
At each point, the system records electrical activity. The computer notes the catheter’s exact 3D position and the electrical signal’s characteristics at that location. As data from more points accumulates, the 3D picture becomes increasingly detailed.
The process takes 10-30 minutes depending on how detailed a map is needed. For simple rhythm problems, a basic map with a few hundred points suffices. For complex problems like atrial fibrillation, doctors might collect data from thousands of points, creating extremely detailed maps.
The resulting 3D model shows your heart chamber’s shape and size. Colors indicate when each area activates electrically. Watching the map play through a heartbeat looks like watching colored waves spreading across the chamber.
For some rhythm problems, the map reveals circular patterns—signals traveling in loops rather than spreading normally. These re-entry circuits cause many arrhythmias. The map shows exactly where the loop is located.
For other problems, the map shows a specific spot firing signals too rapidly—a focal source. The map pinpoints this location.
Once problem areas are identified, doctors use the map to guide ablation. They position the ablation catheter at targeted spots and deliver energy. The system marks each ablation spot on the map. This prevents missing areas and shows exactly where treatment was delivered.
After ablation, doctors create new maps to confirm problem areas are eliminated. The electrical patterns should now look normal. If abnormal patterns persist, additional ablation is performed.
The real-time tracking reduces X-ray use. Instead of constantly using X-rays to see catheter positions, doctors watch catheter positions on the 3D map. X-rays are used periodically to confirm positions but not continuously.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
3D mapping provides significant benefits compared to older techniques.
Precision is dramatically improved. Instead of estimating problem locations, doctors see exact spots on detailed maps. This allows targeted treatment of just the problematic tissue.
Completeness of treatment improves. For conditions requiring lines of ablation—like atrial fibrillation—the map shows whether lines are continuous or have gaps. Gaps can be filled immediately, reducing the chance of rhythm problems recurring.
Safety increases because healthy tissue is preserved. Unnecessary ablation is avoided when doctors can clearly distinguish normal from abnormal areas.
Procedure times often decrease with mapping. Finding problem areas quickly and treating them precisely means less time overall, though creating detailed maps adds some time upfront.
Success rates improve. Studies show better outcomes when ablation is guided by 3D mapping compared to traditional methods, particularly for complex rhythm problems.
Radiation exposure decreases significantly. Traditional ablation requires continuous X-ray use. With 3D mapping, X-rays are used minimally, protecting both you and medical staff.
Education and communication improve. Doctors can show you your 3D map afterward, explaining exactly what was found and what was treated. This helps you understand your condition better.
Reference: 3D mapping system in the ablation