Tachycardia means that your heart is beating faster than normal while you are at rest. For most adults, a resting heart rate above 100 beats per minute is considered tachycardia.
A fast heartbeat can be a normal response to exercise, stress, excitement, or illness. However, tachycardia refers to situations where your heart rate is inappropriately fast, occurs without a clear reason, or causes symptoms.
Not all tachycardia is dangerous. Some types are temporary and harmless, while others may be caused by an underlying heart rhythm problem that needs medical attention. Understanding the difference helps you know when to be reassured and when to seek care.
- How Your Heart Rate Normally Works
- Symptoms of Tachycardia
- Why Tachycardia Happens
- Sinus Tachycardia: When a Fast Heart Rate Is Normal
- Different Types of Tachycardia
- How Tachycardia Is Diagnosed
- When Tachycardia Becomes a Problem
- Treatment Approach for Tachycardia
- Preventing Recurrence
- Living With Tachycardia
How Your Heart Rate Normally Works
Your heart naturally adjusts its speed based on your body’s needs. When you exercise, feel stressed, or become excited, your heart beats faster to deliver more oxygen-rich blood to your muscles and organs.
Once the trigger passes, your heart rate normally slows back down.
Tachycardia becomes a concern when your heart:
- Continues to beat fast at rest
- Starts suddenly without a clear trigger
- Causes symptoms
In these cases, the fast heartbeat is usually driven by abnormal electrical signals rather than normal body demands.
Symptoms of Tachycardia
The way tachycardia feels can vary widely. Some people clearly feel every fast beat, while others notice only mild or vague symptoms.
It is important to know that how strong your symptoms feel does not always reflect how serious the rhythm problem is.
Common symptoms include:
- A racing or pounding heartbeat
- Palpitations felt in the chest or neck
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest discomfort
- Fatigue or weakness
In more severe cases, tachycardia may cause near-fainting or fainting, especially if blood flow to the brain is temporarily reduced.
Why Tachycardia Happens
Tachycardia can occur for many reasons, and not all of them start in the heart. Sometimes your heart is simply responding appropriately to another condition in your body.
Common causes include:
- Physical activity, anxiety, or emotional stress
- Fever, dehydration, or infection
- Anemia or low oxygen levels
- Thyroid problems
- Caffeine, nicotine, or stimulant use
- Certain medications
In other cases, tachycardia is caused by a heart rhythm disorder, where abnormal electrical pathways or signals inside the heart trigger fast rhythms.
Sinus Tachycardia: When a Fast Heart Rate Is Normal
Not every fast heartbeat is abnormal. In many situations, your heart speeds up for healthy and appropriate reasons. This is called sinus tachycardia.
In sinus tachycardia, the heart rhythm itself is normal — it is simply faster than usual. This commonly happens during:
- Exercise
- Emotional stress
- Fever
- Dehydration
- Pain
- Conditions such as anemia or thyroid disorders
Once the underlying cause is treated or resolves, your heart rate usually returns to normal without the need for heart rhythm treatment.
Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia
In some people, the heart rate remains persistently high at rest, even without an obvious trigger. This is known as Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia.
Although the heart rhythm is normal, the fast rate can cause symptoms such as palpitations, fatigue, and poor exercise tolerance. In these cases, targeted medical treatment may be needed.
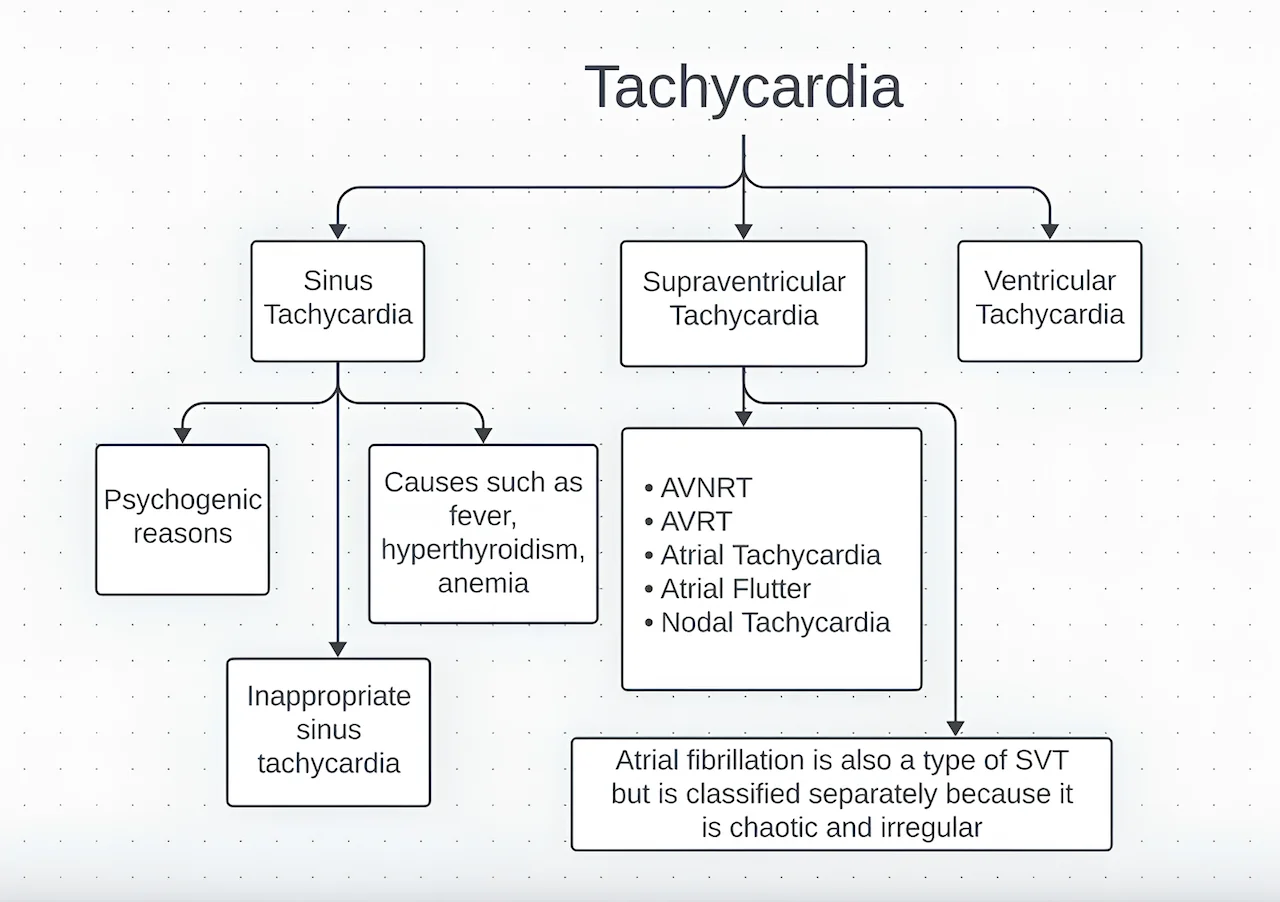
Different Types of Tachycardia
Not all fast heart rhythms are the same. Tachycardia includes several different rhythm patterns, depending on where in the heart the fast rhythm begins.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
SVT starts in the upper chambers of the heart. These episodes usually:
- Begin suddenly
- End suddenly
- Cause fast but regular heartbeats
SVT is common, often occurs in otherwise healthy hearts, and is usually not life-threatening, although symptoms can be intense.
Atrial Fibrillation
In atrial fibrillation, the heartbeat becomes fast and irregular due to chaotic electrical activity in the upper chambers.
This rhythm increases the risk of stroke, making proper diagnosis and long-term management very important.
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia begins in the lower chambers of the heart. These rhythms are generally more serious, especially in people with underlying heart disease.
Because the ventricles pump blood to the body, fast rhythms from this area can significantly reduce circulation and may be life-threatening.
Understanding which type of tachycardia you have is essential, because risk, treatment, and long-term outlook differ greatly.
How Tachycardia Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis begins by recording your heart rhythm using an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Because some episodes are brief or infrequent, longer-term rhythm monitoring may be needed. Additional tests may help evaluate heart structure, blood flow, and possible triggers.
The goal is not only to confirm tachycardia, but also to identify its cause and guide the most appropriate treatment.
When Tachycardia Becomes a Problem
Occasional fast heartbeats are common and often harmless.
Tachycardia becomes more concerning when it:
- Happens frequently
- Lasts for long periods
- Causes significant symptoms
- Occurs in people with heart disease
If left untreated, persistent tachycardia can place strain on the heart and, over time, weaken the heart muscle.
Treatment Approach for Tachycardia
Treatment depends entirely on the underlying cause of your fast heart rate.
In many cases, no specific heart treatment is needed. If tachycardia is triggered by factors such as dehydration, fever, infection, stress, anemia, or thyroid problems, treating these conditions often allows your heart rate to return to normal.
Lifestyle adjustments may also play an important role. Staying well hydrated, reducing caffeine and stimulant intake, managing stress, and improving sleep can significantly reduce episodes in many people.
If tachycardia is caused by a heart rhythm disorder, treatment options may include:
Medications
Certain medications can help:
- Slow the heart rate
- Stabilize the heart’s electrical system
- Reduce the frequency and intensity of fast rhythm episodes
These medications are chosen carefully based on your specific rhythm type, symptoms, age, and overall health.
Catheter Ablation
For people with frequent symptoms, poor medication tolerance, or recurrent episodes, catheter ablation may be recommended.
During this minimally invasive procedure, thin flexible tubes are guided into the heart. The abnormal electrical pathway causing the fast rhythm is precisely located and safely eliminated using controlled energy.
In many rhythm disorders, catheter ablation can permanently cure tachycardia, allowing you to stop long-term medications and return to normal life.
Treatment of Underlying Heart Disease
If tachycardia occurs in the setting of structural heart disease, heart failure, or previous heart injury, treatment also focuses on improving overall heart function and preventing future rhythm problems.
This may include optimized medical therapy, lifestyle changes, and in selected cases, device-based treatments.
Emergency Treatment
In rare situations, very fast or unstable tachycardia may require urgent treatment in the emergency setting. This can include medications given through a vein or, in selected cases, controlled electrical cardioversion to restore normal rhythm.
Individualized Care
The most important aspect of tachycardia treatment is that it is tailored specifically to you. Your symptoms, test results, lifestyle, and overall health all guide the treatment plan.
The goal is not only to slow your heart rate, but to restore a rhythm that allows your heart to pump efficiently, safely, and comfortably — so you can live an active and confident life.
Preventing Recurrence
Many forms of tachycardia can be influenced by daily habits. Helpful steps include:
- Staying well hydrated
- Managing stress
- Limiting caffeine and stimulants
- Getting enough sleep
- Treating underlying medical conditions
Understanding your personal triggers and keeping regular medical follow-up can greatly reduce recurrence.
Living With Tachycardia
Living with tachycardia can feel unsettling, especially when episodes are unpredictable. Learning about your condition, recognizing triggers, and understanding your treatment plan helps reduce anxiety and improves confidence.
With proper care, most people with tachycardia lead full, active, and unrestricted lives.
Reference: Tachycardia