Atrial fibrillation (AFib) ablation is a catheter-based procedure used to reduce or eliminate episodes of atrial fibrillation by treating the areas of the heart that trigger and sustain this irregular rhythm. The goal of AFib ablation is to restore and maintain a more regular heart rhythm, relieve symptoms, and improve quality of life.
AFib ablation does not involve open-heart surgery. It is performed using thin catheters guided to the heart through blood vessels, most commonly from the groin.
- When Is Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Recommended?
- How Atrial Fibrillation Develops
- What Is Pulmonary Vein Isolation?
- Preparing for AFib Ablation
- What Happens During AFib Ablation?
- What Will I Feel During and After the Procedure?
- Recovery After AFib Ablation
- Medications After AFib Ablation
- Risks of AFib Ablation
- How Successful Is AFib Ablation?
- In Summary
When Is Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Recommended?
AFib ablation is considered when atrial fibrillation causes symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, reduced exercise capacity, or decreased quality of life. It is often recommended when medications fail to adequately control the rhythm or cause unacceptable side effects.
In some patients, ablation may be offered earlier in the course of atrial fibrillation as part of a rhythm-control strategy, particularly when maintaining normal rhythm is an important treatment goal.
The decision to proceed with ablation is individualized and depends on the type of AFib (paroxysmal or persistent), symptom burden, duration of AFib, size of the atria, and overall heart health.
How Atrial Fibrillation Develops
In atrial fibrillation, the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat in a fast and irregular manner instead of contracting in an organized way. In most patients, AFib is triggered by abnormal electrical signals that originate near the pulmonary veins, which carry blood from the lungs into the left atrium.
These abnormal signals can repeatedly disrupt the heart’s normal rhythm, leading to ongoing or recurrent atrial fibrillation.
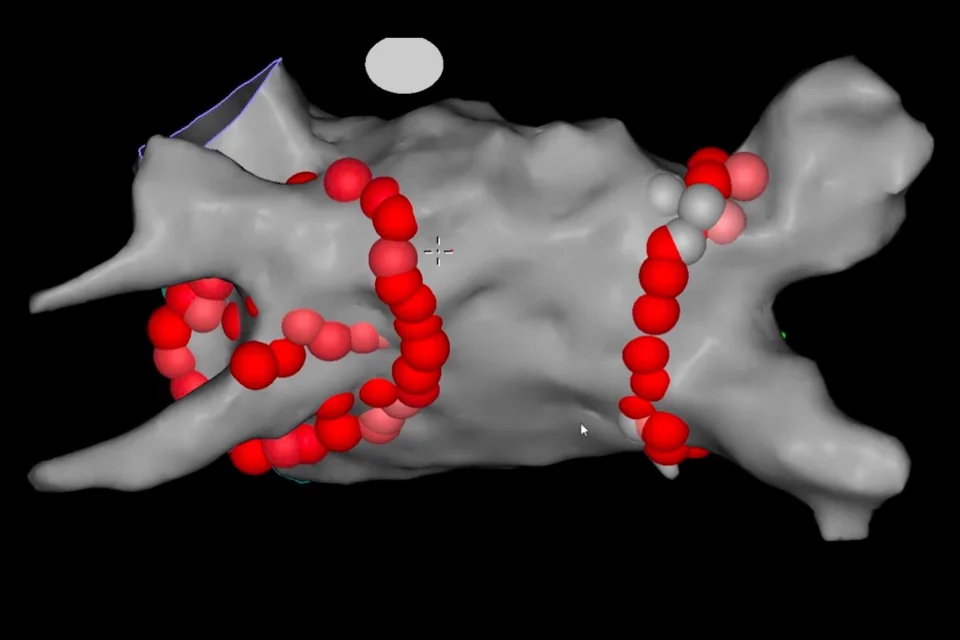
What Is Pulmonary Vein Isolation?
The cornerstone of AFib ablation is a technique called pulmonary vein isolation (PVI). This means electrically isolating the pulmonary veins from the rest of the left atrium so that abnormal signals from these areas can no longer trigger atrial fibrillation.
Pulmonary vein isolation does not block blood flow. It is an electrical treatment that prevents abnormal impulses from entering the atrium while preserving normal circulation.
In some patients—especially those with persistent or long-standing AFib—additional ablation beyond PVI may be needed. Your doctor will explain the planned strategy based on your specific situation.
Preparing for AFib Ablation
Before AFib ablation, several tests are performed to confirm the diagnosis and plan the procedure safely. These may include heart rhythm monitoring, echocardiography, blood tests, and sometimes advanced imaging of the heart.
You may be instructed to adjust or temporarily stop certain medications before the procedure. Blood-thinning medication is managed carefully to reduce stroke risk. Fasting for several hours before the procedure is usually required, and clear instructions are provided in advance.
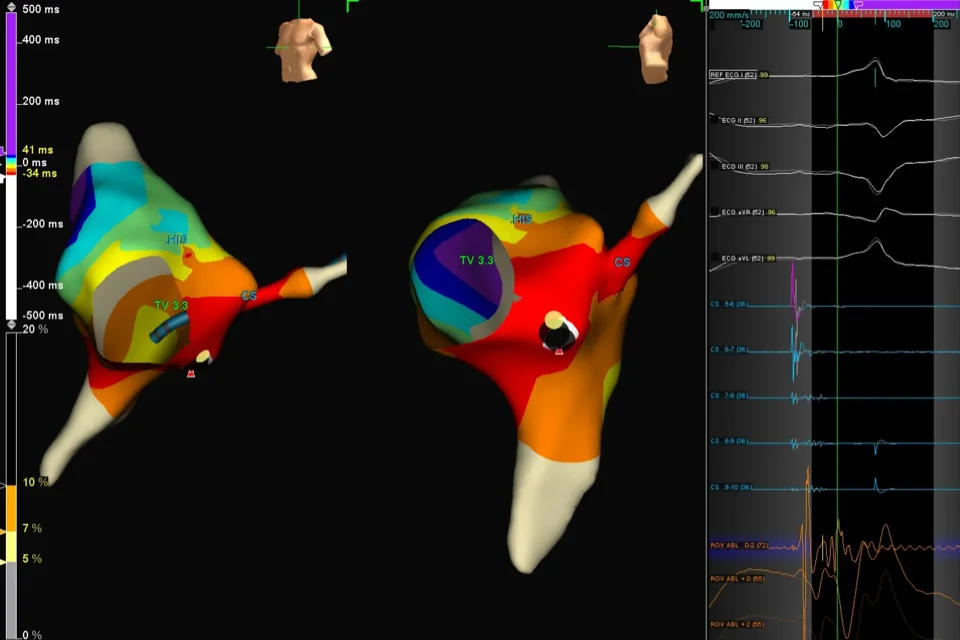
What Happens During AFib Ablation?
AFib ablation is performed in a specialized hospital unit. Most patients receive sedation and are relaxed and sleepy during the procedure, while some procedures are performed under general anesthesia.
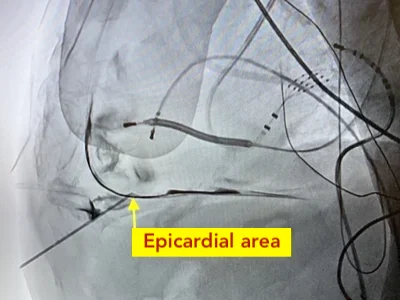
Catheters are inserted through blood vessels—most commonly in the groin—and guided to the heart. Once the pulmonary veins and other relevant areas are identified, controlled energy is delivered through the catheter to isolate abnormal electrical signals.
Different types of energy may be used, including radiofrequency ablation (heat), cryoablation (freezing), and in selected cases pulsed field ablation (PFA), a newer technology that uses short electrical pulses. The choice of technique depends on anatomy, AFib type, and treatment strategy.
The procedure typically lasts several hours.
What Will I Feel During and After the Procedure?
Because sedation or anesthesia is used, most patients do not feel pain during the procedure. You may feel mild pressure at the catheter insertion site.
After the procedure, it is common to feel tired. Mild chest discomfort, throat soreness (if general anesthesia was used), or temporary palpitations may occur. Short episodes of irregular rhythm can happen during the healing period and do not necessarily mean the ablation was unsuccessful.
Recovery After AFib Ablation
Most patients stay in the hospital overnight and return home the next day. Normal daily activities can usually be resumed within a few days, although strenuous exercise is limited for a short period.
Your medical team will provide specific guidance on activity, wound care, and follow-up appointments.
Medications After AFib Ablation
Some patients continue antiarrhythmic medications temporarily after ablation while the heart heals. These medications are often reassessed and may be reduced or stopped later.
Blood-thinning medication is managed based on stroke risk, not simply on whether AFib appears to be eliminated. Many patients need to continue anticoagulation even after successful ablation, depending on individual risk factors.
Risks of AFib Ablation
AFib ablation is a commonly performed and generally safe procedure in experienced centers. As with any invasive treatment, risks exist and are discussed in advance. Serious complications are uncommon.
Careful planning, imaging, and modern ablation technologies have significantly improved the safety of the procedure.
How Successful Is AFib Ablation?
Success rates depend on the type of atrial fibrillation and individual heart characteristics.
In paroxysmal (intermittent) AFib, approximately 70–80% of patients experience significant reduction or elimination of AFib episodes after one procedure, with higher success after repeat ablation if needed.
In persistent AFib, success rates are lower, and more than one procedure may be required. Even when AFib is not completely eliminated, ablation often reduces symptom burden and improves quality of life.
In Summary
Atrial fibrillation ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that targets the electrical triggers of AFib, most commonly through pulmonary vein isolation. It is recommended for patients with symptomatic AFib when medications are ineffective or not well tolerated, or when long-term rhythm control is desired. With appropriate patient selection and modern techniques—including newer options such as pulsed field ablation—AFib ablation can significantly improve symptoms, reduce arrhythmia burden, and enhance quality of life.
Reference: Atrial fibrillation ablation