Cryoablation is a catheter-based ablation technique used to treat certain heart rhythm disorders by freezing the tissue responsible for the abnormal electrical signals. By applying controlled cold energy, cryoablation creates a small, targeted area of electrical block, preventing the arrhythmia from starting or continuing.
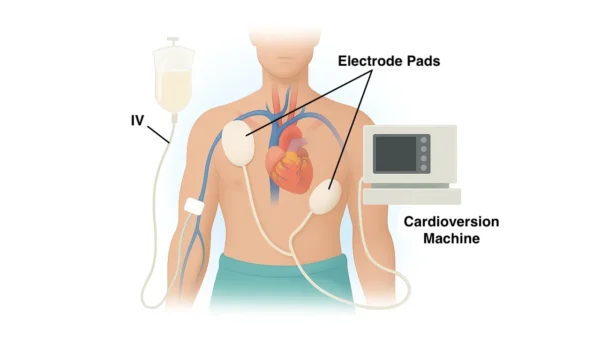
Cryoablation is one of several energy options used in cardiac ablation. It does not involve open-heart surgery and is performed using thin catheters guided to the heart through blood vessels.
What Is Cryoablation?
In cryoablation, the tip of a special catheter is cooled to very low temperatures. This freezing process temporarily disables electrical activity during application and then creates a lasting effect once the tissue is fully treated.
One unique feature of cryoablation is that the tissue can be tested while frozen before the effect becomes permanent. This allows the operator to confirm the desired effect and adds an extra margin of safety in certain locations.
Which Arrhythmias Are Treated With Cryoablation?
Cryoablation is most commonly used in the treatment of:
- Atrial fibrillation, particularly through a technique called pulmonary vein isolation using a cryoballoon
- Certain supraventricular tachycardias (SVT), especially when treatment is close to sensitive structures
- Selected atrial arrhythmias, depending on anatomy and operator preference
Its most established role is in atrial fibrillation ablation, where cryoballoon technology allows efficient and consistent isolation of the pulmonary veins.
Cryoablation in Atrial Fibrillation
In atrial fibrillation, abnormal electrical signals often originate near the pulmonary veins. Cryoablation can be performed using a balloon-based system that seals the opening of each pulmonary vein and delivers freezing energy around it.
This approach allows the pulmonary veins to be electrically isolated in a relatively uniform and reproducible way, making cryoablation a widely used option for AFib ablation in appropriate patients.
How Cryoablation Is Performed
Cryoablation is performed in a specialized electrophysiology laboratory. Catheters are inserted through blood vessels—usually in the groin—and guided to the heart.
Once positioned at the target area, freezing energy is delivered for a defined period. The total procedure time varies depending on the arrhythmia being treated but is comparable to other catheter ablation techniques.
Recovery After Cryoablation
Recovery after cryoablation is similar to recovery after other catheter ablation procedures. Most patients stay in the hospital overnight and return home the next day.
Temporary fatigue, mild chest discomfort, or brief rhythm irregularities can occur during the healing period and usually resolve on their own.
Advantages and Limitations of Cryoablation
Cryoablation offers a predictable lesion shape and is associated with stable catheter positioning during freezing. These features make it particularly useful in specific anatomical situations, such as pulmonary vein isolation.
However, cryoablation is not suitable for all arrhythmias or all heart locations. Other energy sources may be preferred depending on the rhythm problem, heart anatomy, and treatment goals.
In Summary
Cryoablation is a freezing-based cardiac ablation technique used to treat certain heart rhythm disorders, most commonly atrial fibrillation. By creating controlled electrical block through cold energy, cryoablation can effectively eliminate abnormal rhythm triggers in selected patients. It is one of several established tools used in modern catheter ablation and is chosen based on individual clinical needs.
You may also like to read these:
Radiofrequency Ablation in Heart
Reference: Cryo ablation