Lifestyle, balanced diet, and regular exercise play important roles in reducing the risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib) and maintaining heart health. Since atrial fibrillation can lead to serious problems such as stroke and heart failure, maintaining a regular and balanced life is quite important. Proper diet is a fundamental building block for a healthy heart. A balanced diet consisting of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps control atrial fibrillation episodes.
Regular exercise also supports heart health and improves overall quality of life. Therefore, adopting and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits is an important part of treatment for atrial fibrillation patients.
What is atrial fibrillation (AFib)?
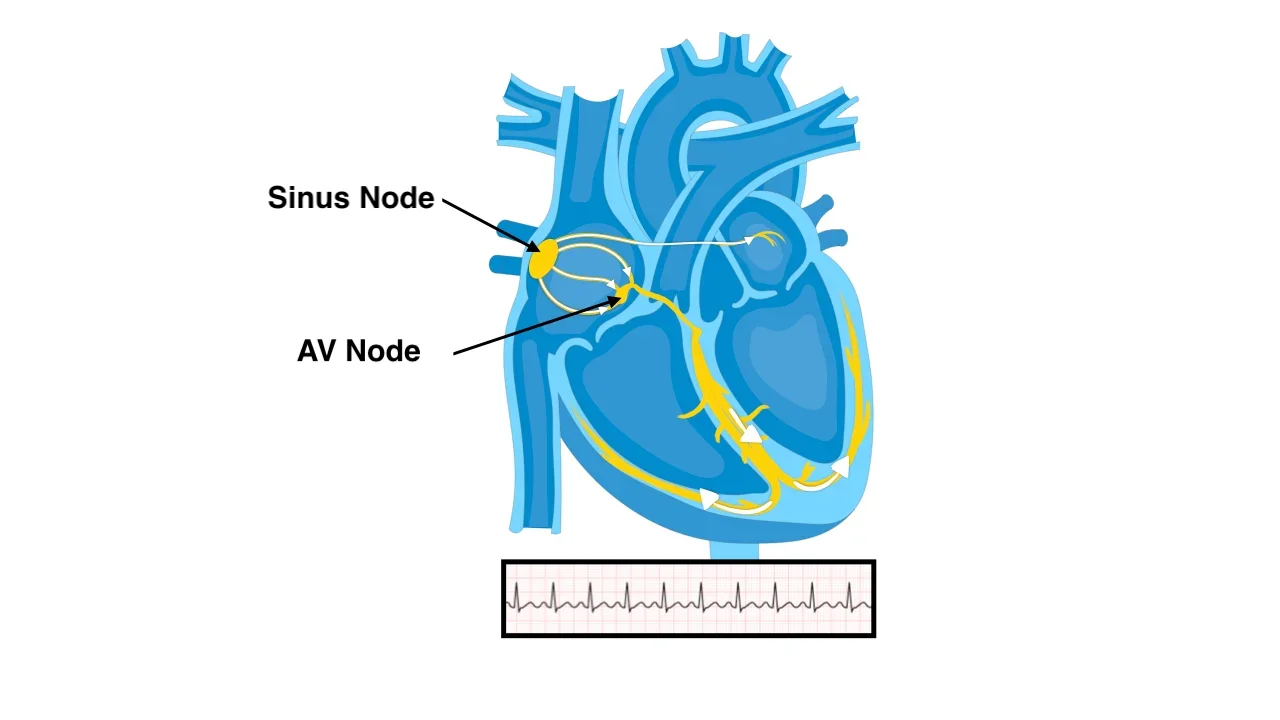
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a heart condition characterized by an irregular and usually rapid heart rhythm. In a normal, healthy heart, the upper chambers (atria) and lower chambers (ventricles) work in coordination to pump blood efficiently throughout the body. However, in atrial fibrillation, the atria are exposed to chaotic electrical signals, causing them to quiver or “fibrillate” instead of contracting regularly and coordinately. This irregular heart rhythm can have serious consequences because it can lead to blood clots forming, which can travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Atrial fibrillation also increases the risk of heart failure and other cardiovascular complications.
Factors such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and certain lifestyle habits can contribute to developing atrial fibrillation. By addressing these risk factors through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes, we can maintain a healthy heart and reduce the risks of atrial fibrillation.
What Should Be the Diet for Atrial Fibrillation?
People with atrial fibrillation (AFib) should follow a heart-healthy diet plan. Daily salt consumption should be reduced (less than 5 grams), and salty snacks and processed foods should be avoided. Caffeinated beverages such as coffee, cola, and energy drinks should be limited. Olive oil should be preferred over saturated fats, and fried foods should be avoided. Fish should be consumed at least twice a week to increase omega-3 intake. A diet rich in vegetables and fruits is essential. Whole grain products and high-fiber foods should be preferred.
Regular eating habits should be established, and meal skipping should be avoided. Instead of consuming large portions at once, meals should be divided into smaller portions throughout the day. Daily water intake should be at least 2-2.5 liters. Heavy meals should be avoided late in the evening. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, and excess weight should be managed through proper diet. Regular doctor check-ups should be attended, and the recommended dietary program should be followed strictly.
A balanced and heart-healthy diet plays a crucial role in maintaining heart health and reducing the risk of atrial fibrillation. Dietary choices can directly affect the development and progression of this condition.
AFib and exercise
The safest and most beneficial exercise option for AFib patients is daily regular brisk walking. Additionally, gentle swimming and low-resistance cycling activities can be preferred. Low-intensity activities such as yoga, gentle stretching exercises, relaxation techniques, and tai chi support heart health. These activities should be performed regularly at moderate intensity for 20-30 minutes per day, 3-5 days per week. Doctor approval should always be obtained before starting any exercise program, and heart rhythm should be monitored regularly during exercise.
Things to Consider While Exercising:
- Start exercise slowly and increase gradually
- Avoid excessive fatigue
- Monitor pulse and rhythm
- Take breaks if symptoms like shortness of breath or dizziness occur
- Avoid exercise in very hot or cold weather
- Ensure adequate fluid intake before and after exercise
- Start the program with doctor approval
Goal:
- 3-5 days per week
- 20-30 minutes each time
- Moderate intensity activity
- Regular and continuous exercise program
When done regularly and under control, exercise improves the quality of life for AF patients and supports heart health.
AFib and Lifestyle Changes
Diet and Weight Control
Healthy and balanced diet is of great importance for AFib patients. Losing excess weight, limiting salt consumption, and keeping caffeine intake under control play critical roles in managing the disease. Paying attention to regular meal times and portion control are also important parts of the dietary regimen.
Exercise and Activity
Regular physical activity is one of the important factors that improve the quality of life for AFib patients. Daily brisk walks and moderate-intensity exercises are particularly recommended. However, it’s necessary to avoid activities that could cause excessive fatigue and take appropriate rest breaks. It’s important for each patient to determine an activity program suitable for their physical capacity.
Control of Harmful Habits
Completely quitting smoking and restricting alcohol consumption are of great importance in controlling the disease. Learning and applying relaxation techniques for stress management and establishing a regular sleep pattern also positively affect the course of the disease. These changes also contribute to improving overall health status.
Monitoring and Control
Regular medication use and attention to check-ups are essential for successful disease management. Regular use and monitoring of blood thinners, blood pressure monitoring, and pulse and rhythm control should be performed regularly. Going to doctor check-ups at specified intervals and getting recommended tests is critically important for monitoring the course of the disease.
These lifestyle changes are an indispensable part of AFib treatment and significantly improve patients’ quality of life. Making these changes sustainable and integrating them into daily life is very important for long-term success.
Conclusion:
Atrial fibrillation or AFib is a complex and potentially serious heart condition. However, by making strategic changes in your diet, exercise routine, and lifestyle, you can take proactive steps to manage and even prevent this condition, ultimately supporting a healthier heart.
Implementing a balanced and healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation, improve heart rate control, and lower the risk of AFib. Regular physical activity, including a combination of aerobic and resistance training, can also play an important role in managing heart rhythm and improving overall cardiovascular function.
Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, managing stress, maintaining a healthy sleep routine, and reducing alcohol and caffeine consumption can further contribute to reducing the risk of AFib and promoting a healthier heart.
Remember, small, sustainable changes can have a significant impact on your overall health.
Reference: Lifestyle Modification Approaches to Atrial Fibrillation