Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) is an advanced pacing treatment used to improve the coordination of heart contractions in selected patients with heart failure and electrical conduction delay. In these patients, the heart’s electrical signals reach different parts of the ventricles at different times, causing the heart muscle to contract in an uncoordinated and inefficient manner. CRT addresses this problem by restoring synchronized ventricular activation, allowing the heart to pump more effectively.
CRT is not simply a treatment for slow heart rate. It is a targeted heart failure therapy aimed at correcting abnormal electrical timing that contributes directly to reduced cardiac performance and worsening symptoms.
- Why Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Is Needed
- How Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Works
- CRT Devices and Configurations
- Who Is a Candidate for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy?
- The CRT Implantation Procedure
- Recovery and Early Follow-Up After CRT Implantation
- Benefits of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
- Limitations and Non-Response
- Living With a CRT Device
- In Summary
Why Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Is Needed
In many patients with heart failure, especially those with left bundle branch block or a widened QRS complex on ECG, electrical activation of the ventricles is delayed and uneven. Instead of contracting together, the right and left ventricles contract out of phase. This electrical dyssynchrony leads to reduced pumping efficiency, increased mitral valve leakage in some patients, and progressive enlargement and weakening of the heart.
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy is designed to correct this electrical mismatch. By coordinating ventricular contraction, CRT reduces mechanical inefficiency and helps reverse adverse remodeling of the heart muscle.
How Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Works
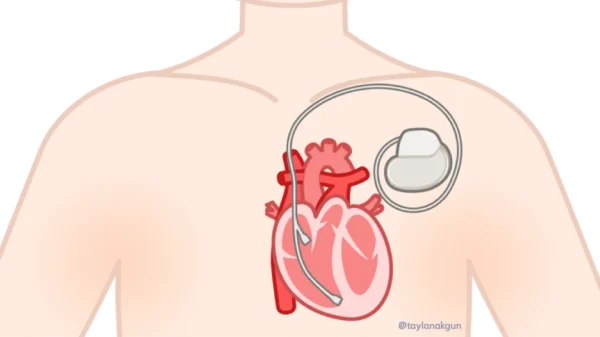
A CRT device continuously monitors the heart’s rhythm and delivers precisely timed electrical impulses to both ventricles, synchronizing their contraction. This coordinated activation improves stroke volume and reduces the workload on the heart.
Rather than pacing continuously, modern CRT systems provide support only when needed and adjust pacing parameters dynamically. This allows therapy to be tailored to each patient’s intrinsic rhythm and physiological needs.
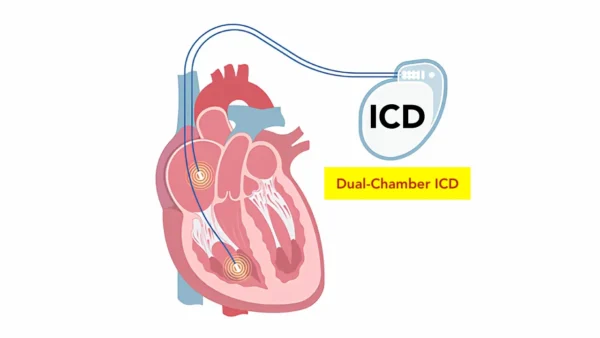
CRT Devices and Configurations
CRT devices are available in two main configurations, selected according to arrhythmia risk and clinical profile.
Some patients receive a CRT pacemaker (CRT-P), which provides biventricular pacing without defibrillation capability. Others require a CRT defibrillator (CRT-D), which combines resynchronization therapy with protection against life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias. The choice depends on individual risk of sudden cardiac death rather than heart failure severity alone.
Who Is a Candidate for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy?
CRT is offered to carefully selected patients with symptomatic heart failure despite optimal medical therapy, reduced left ventricular function, and evidence of electrical conduction delay. The presence of a widened QRS complex—particularly with left bundle branch block morphology—strongly predicts response to therapy.
Patient selection is critical. When electrical dyssynchrony is a major driver of heart failure, CRT can produce substantial and sustained clinical benefit.
The CRT Implantation Procedure
CRT implantation is a minimally invasive procedure performed in a cardiac electrophysiology or pacing laboratory, usually under local anesthesia with conscious sedation.
During the procedure, pacing leads are positioned in the right atrium and right ventricle, along with a specialized lead that stimulates the left ventricle via the coronary sinus. Lead position and electrical performance are carefully tested to achieve optimal synchronization before the device is connected and implanted under the skin.
The procedure typically takes two to three hours, depending on anatomy and technical complexity.
Recovery and Early Follow-Up After CRT Implantation
Recovery after CRT implantation is generally smooth. Most patients are discharged within one to two days. Temporary discomfort or bruising at the implantation site is common and resolves quickly.
In the weeks following implantation, arm movement on the device side is limited to allow proper lead stabilization. Follow-up visits focus on device optimization, as fine-tuning pacing parameters is essential to achieving the full benefit of resynchronization therapy.
Benefits of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
In appropriately selected patients, CRT can lead to meaningful improvement in daily life. Many patients experience reduced shortness of breath, increased exercise tolerance, fewer heart failure hospitalizations, and improved quality of life. Over time, CRT may also promote reverse remodeling of the heart, improving pumping function and long-term outcomes.
Importantly, the benefits of CRT often increase gradually over several months rather than appearing immediately.
Limitations and Non-Response
Although CRT is highly effective in selected patients, not everyone responds equally. Some patients experience limited improvement despite appropriate implantation. This highlights the importance of careful patient selection, optimal lead placement, and ongoing device optimization.
Non-response does not mean treatment failure in all cases, and further adjustments or evaluation may improve outcomes.
Living With a CRT Device
Patients with CRT devices require regular follow-up to monitor battery life, pacing performance, and clinical response. Many modern systems support remote monitoring, allowing early detection of issues and reducing the need for frequent clinic visits.
Battery life typically ranges from six to ten years, after which the generator can be replaced in a relatively simple procedure.
In Summary
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy is a specialized pacing treatment that improves ventricular coordination in selected patients with heart failure and electrical conduction delay. By restoring synchronized contraction, CRT enhances cardiac efficiency, reduces symptoms, and improves quality of life. When carefully indicated and expertly optimized, CRT is a cornerstone therapy in modern heart failure management.
Reference: Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy